The Achilles tendon, commonly known as the heel tendon, is a robust “cord” located at the back of the foot.
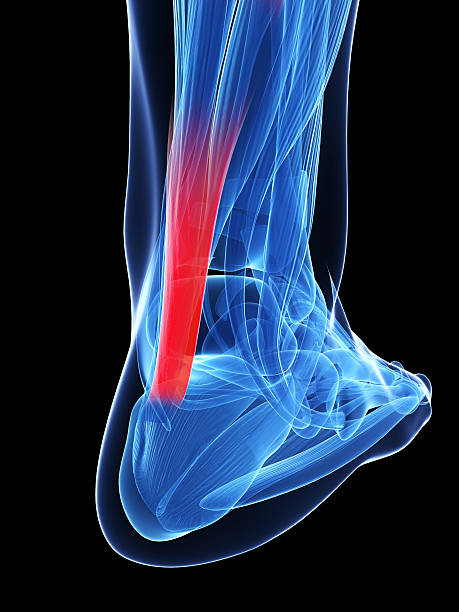
It serves as a vital link connecting the calf muscles (gastrocnemius and soleus) to the calcaneus, imparting the power needed for activities like walking, running, jumping, climbing stairs, and tiptoeing. Contrary to common belief that such injuries primarily afflict athletes, the reality is that this injury can impact individuals across the spectrum, including recreational and amateur athletes. The two prevalent conditions associated with this injury are Achilles tendon rupture or tear and Achilles tendonitis. Achilles tendonitis is essentially an injury to the Achilles tendon, which is situated at the back of the ankle. This crucial tendon links the gastrocnemius muscle to the calcaneus bone and plays a vital role in activities like walking, running, and jumping, enduring significant pressure in our daily movements.
The condition arises when the Achilles tendon and its associated muscles are subjected to excessive use, resulting in irritation and swelling of the tendon. This inflammation occurs due to either overuse or injury.
Types of Achilles Tendon
There are two primary types of Achilles tendonitis:
- Insertion Achilles Tendonitis: This affects the lower part of the tendon, connecting to the heel, and can occur at any age.
- Non-insertive Achilles Tendonitis: This impacts the middle section of the tendon, leading to swelling and thickening. It’s more prevalent in younger individuals and those who engage in regular exercise.
In both forms of Achilles tendonitis, there’s a potential for fibrosclerosis (calcification) to develop in the damaged tendon. This condition underscores the importance of recognizing and addressing the strain on the Achilles tendon to maintain optimal foot health.
Symptoms of Achilles tendon
Symptoms of Achilles tendonitis often manifest as heel pain and swelling in the affected area. If you’re dealing with Achilles tendonitis, it’s advisable to seek medical attention if you:
- Experience Difficulty Bending the Ankle Joint
- Face Discomfort Walking on the Affected Side
- Notice Swelling in the Lower Legs
- Suffer an Injury Resulting in Joint Deformity
- Encounter Nighttime or Rest-Related Ankle Pain
- Endure Ankle Pain Persisting for Several Days
- Observe Signs of Infection, such as Heat, Redness, or Warmth around the Heel
Causes of Achilles tendonitis
- Overuse or Prolonged Pressure on the Affected Area: This includes repetitive small impacts that put stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Sudden Injury: Abrupt injuries can also contribute to the development of Achilles tendonitis.
Risk factors
- Age: Older adults are more prone to developing Achilles tendonitis.
- Bone Spurs: The presence of bone spurs in the heel can irritate the Achilles tendon, causing pain and swelling. This phenomenon becomes more common with age.
- Gender: Men are at a higher risk of experiencing Achilles tendonitis.
- High-Intensity Exercise or Activity: Engaging in activities with intense impact, such as jumping and landing in sports like basketball or running on hard surfaces, increases the likelihood of Achilles tendon injuries.
- High Activity Levels: Running excessively, sudden increases in activity, or running on hilly terrain can elevate the risk of tendon strain or injury.
- Certain Diseases: Individuals with conditions like psoriasis or high blood pressure have an increased susceptibility to Achilles tendonitis.
- Use of Certain Medications: The use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics is associated with a higher prevalence of Achilles tendonitis.
- Obesity: Gaining weight raises the risk of tendon strain.
- Physical Characteristics: Having flat feet can exert additional stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Inadequate Stretching or Warm-up: Insufficient preparation before exercise, leading to a tight gastrocnemius muscle, can contribute to tendon strain.
- Worn Shoes: Wearing shoes with inadequate support can also lead to tendon strain.
Complications and Related Conditions of Achilles Tendon Problem
Achilles tendonitis can escalate to a more serious condition known as Achilles tendon rupture, involving a partial or complete tear of the tendon. This often results in intense pain, necessitating surgical intervention.
While surgery can address tendon issues, it carries inherent risks such as bleeding, infection, and complications from anesthesia. Additional complications from tendon repair surgery may include:
- Nerve Damage
- Difficulty in Healing
- Weakness in the Calves
- Persistent or Recurring Pain in the Feet and Ankles
Individuals may face varying risks based on health, age, and the condition of their feet, leg muscles, and tendons, influencing surgical options. It’s crucial to consult with a doctor to understand specific risks and recommended procedures tailored to individual circumstances.
Prevention of Achilles Tendon Problems
To alleviate heel pain and minimize the risk of this injury, consider the following measures:
- Alternate Activities: Balance high-intensity activities like running and basketball with low-intensity exercises such as swimming and biking to prevent overstrain of the Achilles tendon.
- Gradual Adjustment of Activity: If initiating a new sport or exercise program, start slowly and progressively increase intensity to avoid sudden strain.
- Practice Conditioning: Avoid activities that excessively strain tendons, like running uphill. If pain occurs, cease the activity.
- Daily Stretching: Regular stretching, not just before and after exercise, can maintain the flexibility of the gastrocnemius muscle.
- Strengthen Gastrocnemius Muscles: Enhancing the strength of these muscles helps the Achilles tendon adapt to daily activities and sports-related stresses.
- Thorough Warm-up: Prioritize thorough muscle stretching, especially before engaging in strenuous exercise.
- Wear Supportive Shoes: Choose shoes with proper cushioning and arch support to reduce stress on tendons. Alternatively, consider using orthotics like arch inserts.
Diagnosis of Tendon Achilles Problem
To assess the extent of an Achilles tendon injury and determine appropriate treatment, your doctor may recommend the following diagnostic tests:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This procedure generates detailed cross-sectional images of organs and tissues, revealing any tissue degeneration or breaks in the affected area.
- Ultrasound Scans: These scans can identify inflammation or damage in soft tissues, muscles, blood vessels, tendons, and joints. Ultrasound scans are particularly effective in detecting Achilles tendon injuries.
- X-rays: While not usually required for diagnosing Achilles tendonitis, X-rays may be used to rule out bone-related causes of pain, such as bone spurs or stress fractures in the heel.
Treatments
Your doctor will tailor the treatment for this injury based on the cause, symptoms, and severity of the injury, aiming to alleviate heel pain and promote tendon repair. Non-surgical options may include:
- Heat Packs: Applied to relax muscles and enhance blood flow.
- Ice Packs: Used to minimize swelling.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Taken to relieve pain.
- Physical Therapy: Employed to improve strength and restore mobility.
- Rest: Essential for reducing swelling.
- Steroid Injections: Administered to alleviate swelling.
- Stretching: Targeted at relaxing the gastrocnemius muscles.
Surgery is typically considered in specific circumstances.
- Recurring Injuries and Persistent Pain
- Tendon Rupture or Tear
- Loose Ligaments
Ignoring heel or ankle pain may exacerbate the condition. Seeking consultation with orthopedic specialists ensures an accurate diagnosis and facilitates the development of a suitable treatment plan.